Vue-pinia状态管理
使用Pinia?
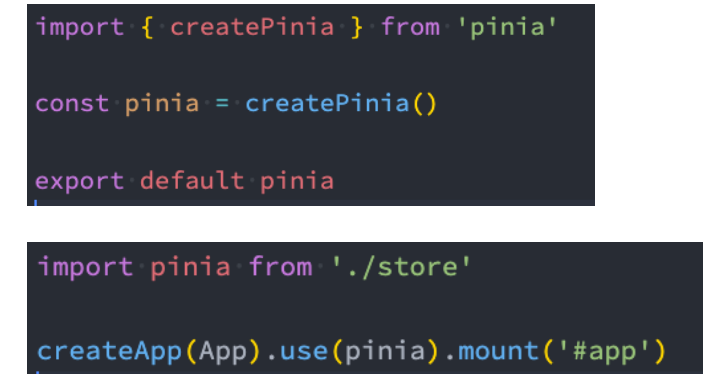
- 使用Pinia之前,我们需要先对其进行安装:
- npm install pinia
- 创建一个pinia并且将其传递给应用程序:
认识Store
- 什么是Store?
- 一个 Store (如 Pinia)是一个实体,它会持有为绑定到你组件树的状态和业务逻辑,也就是保存了全局的状态;
- 它有点像始终存在,并且每个人都可以读取和写入的组件;
- 你可以在你的应用程序中定义任意数量的Store来管理你的状态;
- Store有三个核心概念:
- state、getters、actions;
- 等同于组件的data、computed、methods;
- 一旦 store 被实例化,你就可以直接在 store 上访问 state、getters 和 actions 中定义的任何属性;
定义一个Store
- 定义一个Store:
- 我们需要知道 Store 是使用 defineStore() 定义的,
- 并且它需要一个唯一名称,作为第一个参数传递;
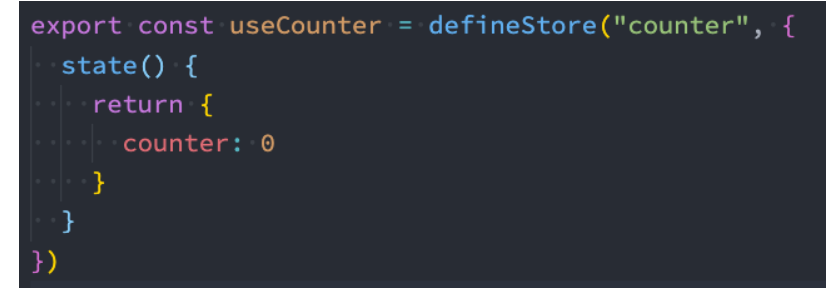
- 这个 name,也称为 id,是必要的,Pinia 使用它来将 store 连接到 devtools
- 返回的函数统一使用useX作为命名方案,这是约定的规范;
使用定义的Store
- Store在它被使用之前是不会创建的,我们可以通过调用use函数来使用Store:
- 注意Store获取到后不能被解构,那么会失去响应式:
- 为了从 Store 中提取属性同时保持其响应式,您需要使用storeToRefs()。
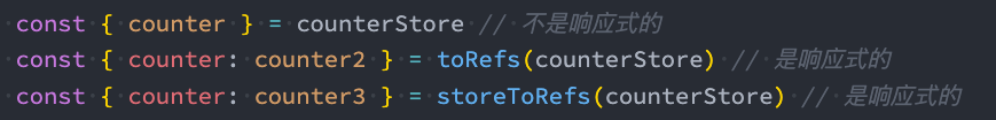
- 为了从 Store 中提取属性同时保持其响应式,您需要使用storeToRefs()。
APP.vue
1 | <template> |
count.js
1 | // 定义关于counter的store |
认识和定义State
- state 是 store 的核心部分,因为store是用来帮助我们管理状态的。
- 在 Pinia 中,状态被定义为返回初始状态的函数;
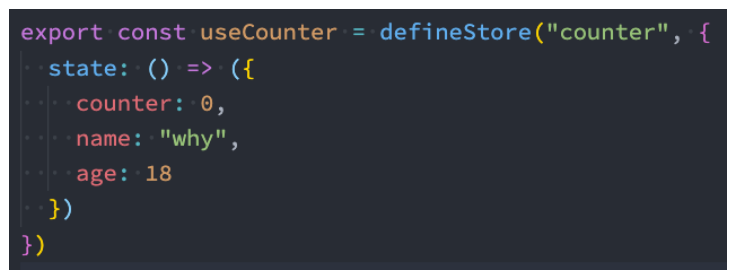
- 在 Pinia 中,状态被定义为返回初始状态的函数;
操作State(一)
- 读取和写入 state:
- 默认情况下,您可以通过 store 实例访问状态来直接读取和写入状态;
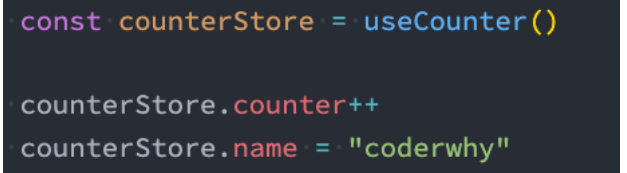
- 默认情况下,您可以通过 store 实例访问状态来直接读取和写入状态;
- 重置 State:
- 你可以通过调用 store 上的 $reset() 方法将状态 重置 到其初始值;

- 你可以通过调用 store 上的 $reset() 方法将状态 重置 到其初始值;
操作State(二)
- 改变State
- 除了直接用 store.counter++ 修改 store,你还可以调用 $patch 方法;
- 它允许您使用部分“state”对象同时应用多个更改;

- 替换State:
- 您可以通过将其 $state 属性设置为新对象来替换 Store 的整个状态:

- 您可以通过将其 $state 属性设置为新对象来替换 Store 的整个状态:
认识和定义Getters
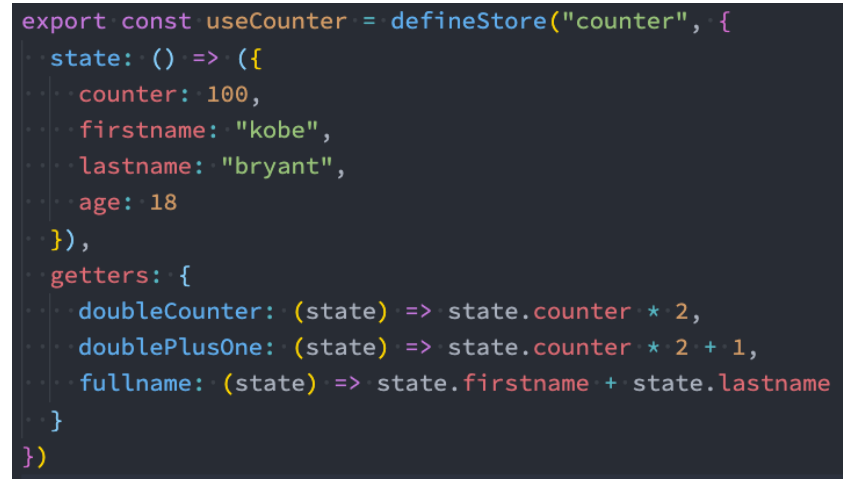
- Getters相当于Store的计算属性:
- 它们可以用 defineStore() 中的 getters 属性定义;
- getters中可以定义接受一个state作为参数的函数;
访问Getters(一)
- 访问当前store的Getters:
- Getters中访问自己的其他Getters:
- 我们可以通过this来访问到当前store实例的所有其他属性;
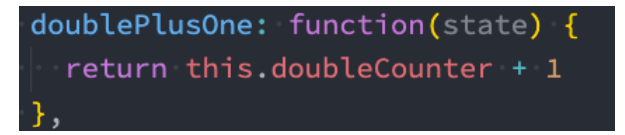
- 我们可以通过this来访问到当前store实例的所有其他属性;
- 访问其他store的Getters:

访问Getters(二)
Getters也可以返回一个函数,这样就可以接受参数 
认识和定义Actions
- Actions 相当于组件中的 methods。
- 可以使用 defineStore() 中的 actions 属性定义,并且它们非常适合定义业务逻辑;

- 可以使用 defineStore() 中的 actions 属性定义,并且它们非常适合定义业务逻辑;
- 和getters一样,在action中可以通过this访问整个store实例的所有操作;
Actions执行异步操作
并且Actions中是支持异步操作的,并且我们可以编写异步函数,在函数中使用await; 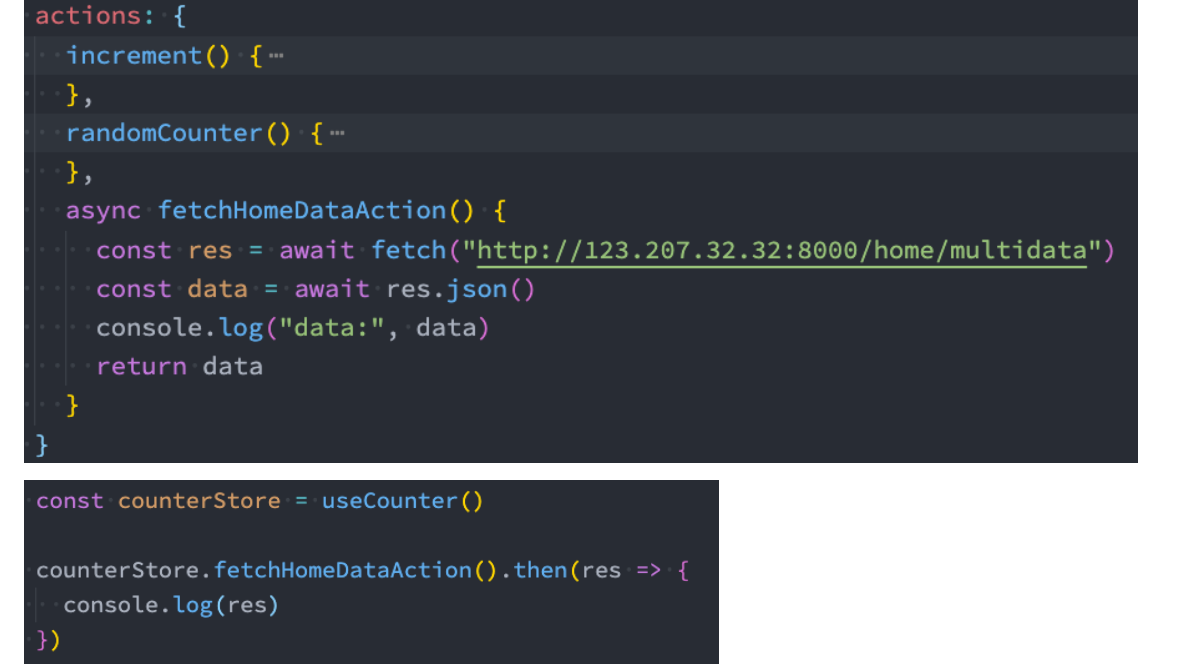
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 十一的博客!
评论






